In addition to the release of the new direction finding feature, the latest version of the Bluetooth® Core Specification introduces some incredible new features, including periodic advertising sync transfer (PAST), which supports periodic advertising over Bluetooth Low Energy. As outlined in the Bluetooth® Core 5.1 Feature Overview, the new periodic advertising sync transfer feature allows another, less-constrained device to perform the synchronization procedure and then pass the acquired synchronization details over a point-to-point Bluetooth Low Energy connection to the other, constrained device.
Legacy Advertising
Previously, all advertising (adv) activities were on three advertising channels: 37 (2402MHz), 38 (2426MHz), and 39 (2480MHz). In figure 1, you can see there are two consecutive adv events. For each adv event, it includes two parts: advertising interval (advInterval) and advertising delay (advDelay).
advInterval defines the interval between two consecutive adv events. The valid range of advInterval is from 20ms to over 10 seconds. In order to avoid interference and physical channel collision for every adv event, an advDelay is added at the end of an adv event, as shown in figure 1. advDelay is a pseudo-random value within a range of 0 to 10ms.
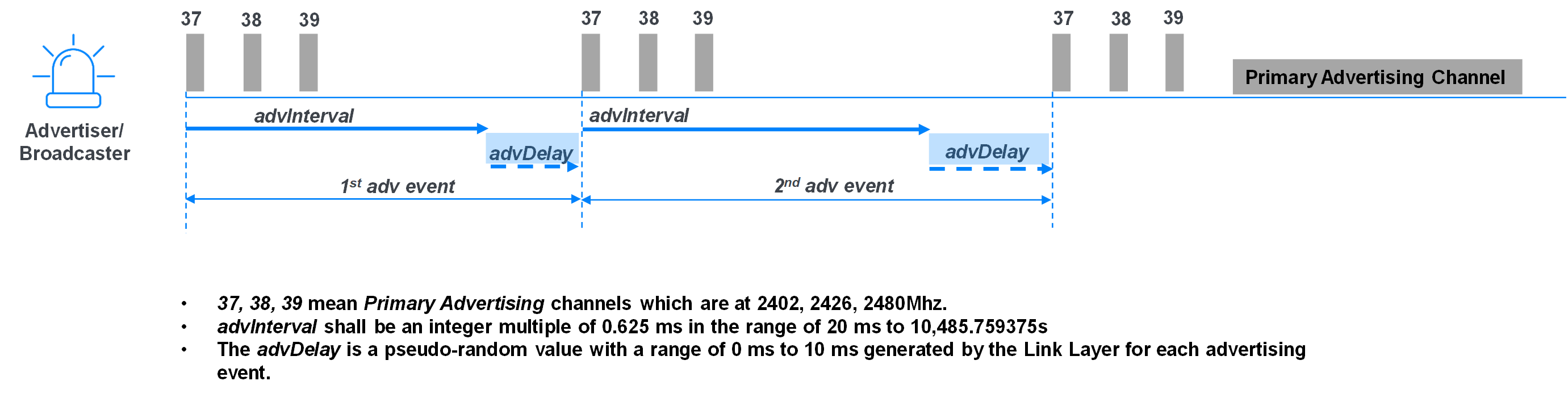
Figure 1 – Legacy Advertising
advDelay makes advertising robust against interference and physical channel collision on the 2.4GHz band. advDelay seems to be very tiny (0~10ms), but after thousands of adv events, the variant will be huge. This restricts some applications because it makes it harder for the scanner to follow the advertiser. Strictly speaking, the scanner can’t synchronize with the advertiser.
If the advertiser can broadcast the advertising packet at a certain pace without any random delay, and the scanner can follow this pace, the scanner will be efficient and save power as this mechanism minimizes the scanning window of the scanner. On the scanner side, it can predict the timing of every advertising packet from the advertiser.
Periodic Advertising
First introduced in an earlier version of the Bluetooth® Core Specification, periodic advertising allows the scanner to sync with the advertiser so the scanner and advertiser would wake up at the same time. The advertiser then sends the adv packet and the scanner turns on the receiver to get the adv packet.
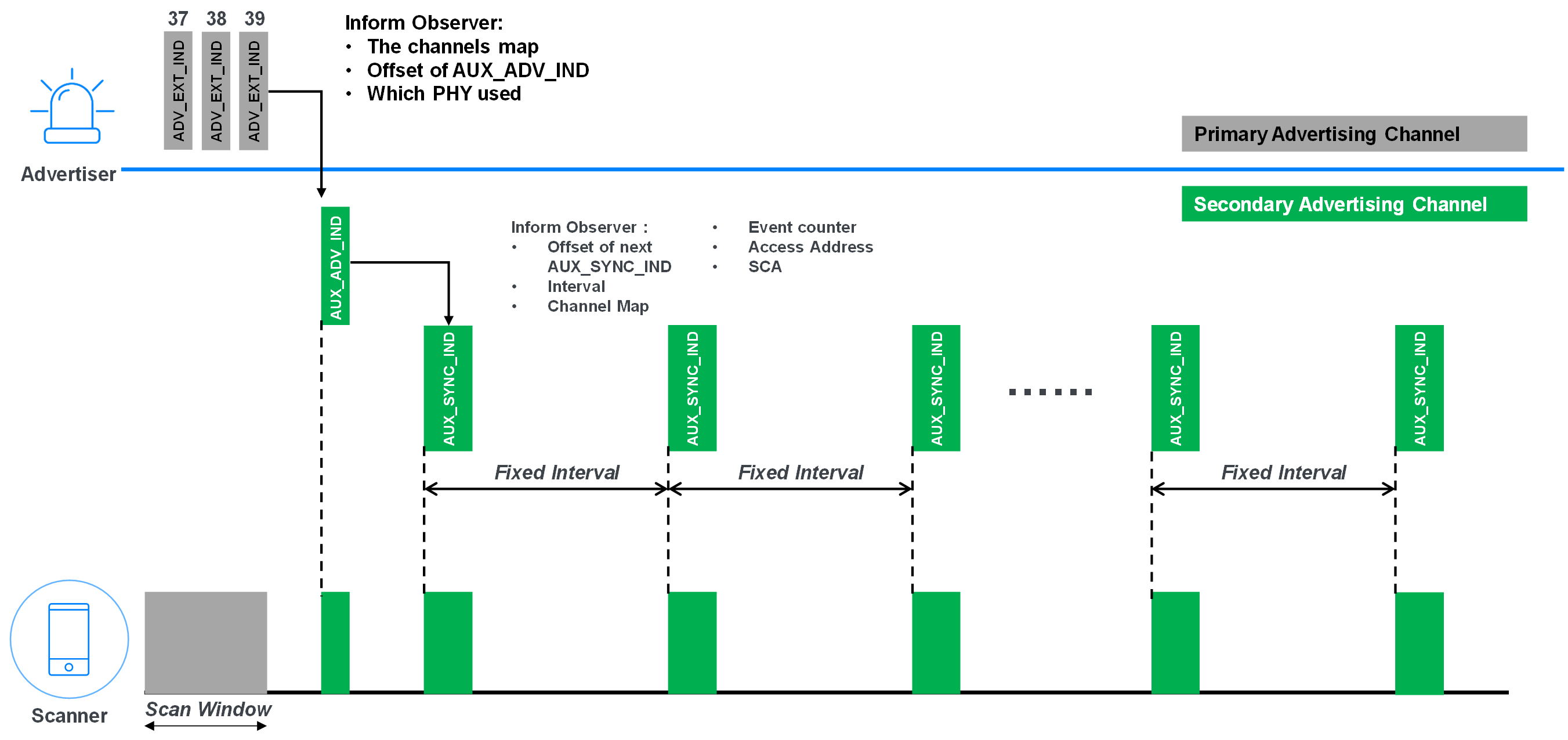
Figure 2 – Periodic Advertising
Figure 2 outlines the whole process of periodic advertising, illustrating the introduction of secondary advertising channels. Three channels (37, 38, and 39) were used as primary advertising channels, and 37 channels were used as secondary advertising channels and data channels.
The gray, borderless area in figure 2 illustrates advertisement over primary advertising channels, and the green, borderless area shows advertisement over secondary advertising channels. It’s obvious that:
- ADV_EXT_IND is over primary advertising channels
- AUX_ADV_IND and AUX_SYNC_IND are over secondary advertising channels
ADV_EXT_IND is over primary advertising channels and is used to indicate that an advertisement will be sent on a secondary advertisement channel. The information in ADV_EXT_IND will inform the scanner:
- Which secondary advertising channel will be used by AUX_ADV_IND
- Which PHY will be used by AUX_ADV_IND, 1M PHY, 2M PHY, or 1M Coded PHY
- When AUX_ADV_IND will be presented on that specified secondary advertising channel
If the scanner is capable of periodic advertising, it will enable its receiver at a specific channel and PHY at a specific time slot.
AUX_ADV_IND is over the secondary advertising channels and is used to indicate a periodic advertising event. The information in AUX_ADV_IND, which points to the first AUX_SYNC_IND, are:
- The offset time of the next periodic advertising packet
- The interval of periodic advertising
- The secondary channel map used through this periodic advertising lifetime
- Access address, etc.
With this information, the scanner can synchronize with the advertiser and they will dance together.
- AUX_SYNC_IND includes the AdvData which needs to be periodically advertised
Angle of Departure Using PAST
Periodic advertising sync transfer (PAST) is an enhancement included in the latest version of the Bluetooth® Core Specification. The scenario below illustrates the case of angle of departure (AoD).
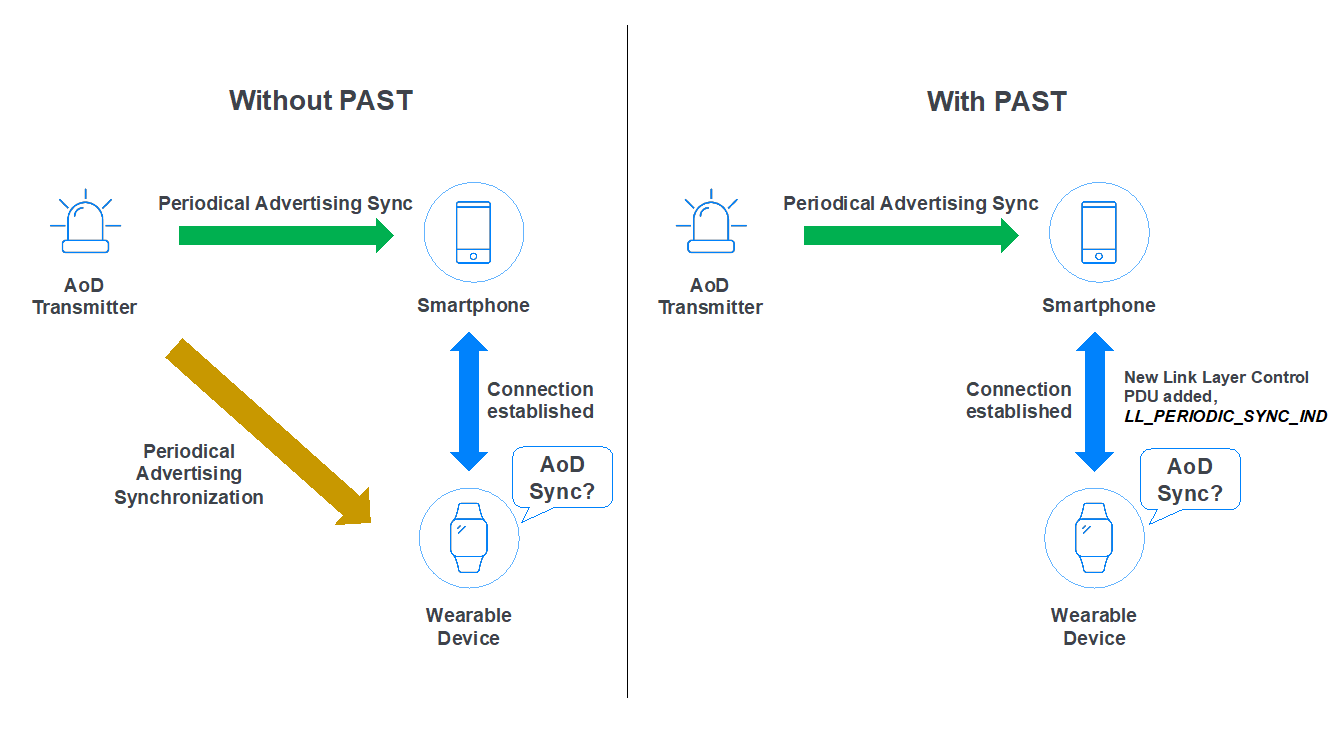
Figure 3 – PAST
As shown in figure 3 on the left, without PAST, the smartphone already has periodic advertising synchronized with an angle of departure (AoD) transmitter. This allows the smartphone to get periodic advertising packets, AUX_SYNC_IND, with Constant Tone Extension (CTE) from the transmitter and interpret them to do IQ sampling and angle calculation.
Meanwhile, the smartphone also establishes a connection with a wearable device. If the wearable device also wants to get periodic advertising packets from the AoD transmitter, the wearable device needs to scan and perform periodic advertising synchronization with an AoD transmitter by itself. This process will take extra time and power consumption to be completed by the wearable device, which is power constrained.
As shown in figure 3 on the right, with PAST, this is different. In the same scenario, if the wearable device wants to scan and perform periodic advertising synchronization with the AoD transmitter with PAST support, the smartphone can transfer the periodic advertising synchronization information to the wearable device over the Bluetooth Low Energy link layer. A new link layer control PDU, LL_PERIODIC_SYNC_IND, is added in the latest version of the Bluetooth® Core Specification to support it. This (PAST) makes it easy and helps power-constrained devices save power.
To learn more about PAST, download the Bluetooth® Core 5.1 Feature Overview.
For more information about the new AoA and AoD methods for direction finding, download this paper on Enhancing Bluetooth Location Services with Direction Finding.
![]()
FEATURED DOWNLOAD
Enhancing Bluetooth Location Services with Direction Finding
Enhancing Bluetooth Location Services with Direction Finding A new Bluetooth direction finding feature allows devices to determine the direction of a Bluetooth signal, thereby enabling the development of Bluetooth proximity solutions that can understand device direction as well as Bluetooth positioning systems that can achieve down to centimeter-level location accuracy.