Perhaps a victim of its own success, the global proliferation of Bluetooth® technology in headsets, phones, watches, and cars has sparked multiple myths about what the technology can and can’t do. In truth, Bluetooth technology powers a wide range of essential solutions, from home automation and indoor navigation to commercial and industrial innovations.
Myth: Bluetooth is Reliable Up to 30 Meters
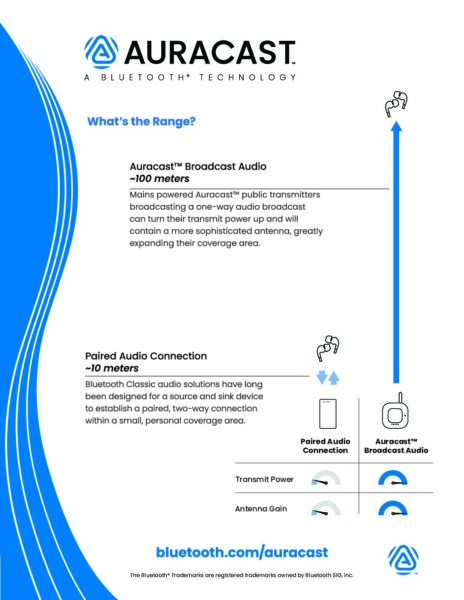
For years, there’s been a widely held opinion that Bluetooth® technology is only good for short-range applications. This is due, in large part, to how the technology is used. Since the most well-known use cases, such as audio and wearables, have design requirements that dictate a shorter range, these developers chose to implement the technology and hardware in a way that delivers a max range of 10 to 30 meters.
In fact, the effective, reliable distance between Bluetooth devices can be greater than a kilometer and can even support reliable remote control of beyond-visual-range (BVR) drones. Bluetooth technology is a fit-for-purpose solution, and several factors can influence the effective range — from radio spectrum and transmit power to antenna gain and path loss.
The variable range is proof of the technology’s versatility. Unlike other wireless technologies, the wide spectrum of achievable and reliable distances gives developers tremendous flexibility to create solutions that meet the precise needs of their target use case. Check out other factors — such as receiver sensitivity, antenna gain, and PHY — that play a role in determining how far Bluetooth range can go.
Myth: Bluetooth Can’t Go Through Walls
Think about when you’re trying to hear someone in the next room. The difference between the volume and clarity of what you can hear differs depending on what the walls are made of. You have an easier time hearing what’s on the other side of a sheetrock wall than you do if the wall is made of concrete. But, in either case, you can still hear a sound if it’s loud enough. The same idea can be applied to radio signals.
Path loss reduces signal strength as it travels through the air. It occurs naturally and is impacted by environmental factors like walls, windows, and other obstacles that might deteriorate the signal. But radio waves can still pass through objects, even concrete walls and floors, meaning that a Bluetooth® signal is not limited to the room you’re in. These barriers will have an impact on the overall range of the signal, but they don’t block it.

Myth: Bluetooth is a Consumer Technology
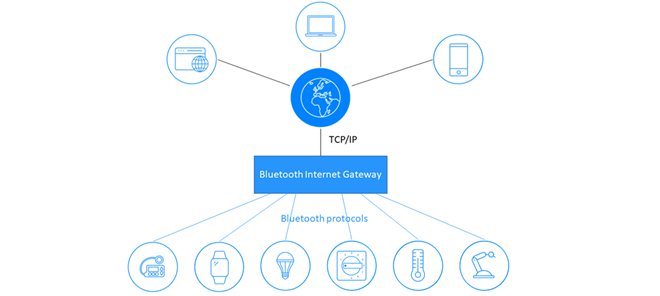
You’re not alone if you think of Bluetooth as a consumer-only technology. There’s widespread misunderstanding about the technology’s commercial and industrial potential. This, again, is due to the history of its use. In the last 20 years, Bluetooth technology created and cultivated hundreds of new global markets with audio streaming and short-range data transfer being two of the most prevalent. And while Bluetooth has made its bread and butter on your headsets, fitness trackers, and smartphones, that is just one aspect of the tech.
All over the world, developers use Bluetooth® technology to achieve wireless connections at distances of more than a kilometer, and these connections are the foundation of a new generation use cases like industrial asset tracking and large-scale sensor networks.
Bluetooth technology can do a lot more than given credit for, and, through innovation in consumer applications, it continues to enhance the lives of millions of people around the world. But, in some ways, its success created a narrow perception of its capabilities. In truth, Bluetooth solutions are used to solve a multitude of less commonly known commercial and industrial challenges.
Check out the Bluetooth range estimator and see how far Bluetooth range can go for you.
![]()
FEATURED TOOL
The Bluetooth Range Estimator
Calculate the expected range between two Bluetooth devices.


















![2312 CES Handout Images FINAL existing pdf 464x600[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/2312_CES_Handout-Images_FINAL-existing-pdf-464x6001-1.jpg)
![2312 CES Handout Images FINAL unlimited pdf 464x600[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/2312_CES_Handout-Images_FINAL-unlimited-pdf-464x6001-1.jpg)