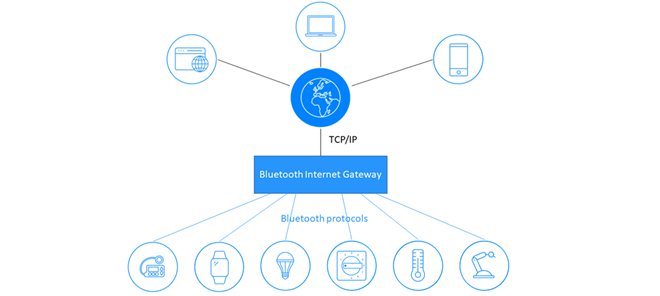
Originally conceived as a wireless alternative to RS-232 data cables, Bluetooth® technology has become the global wireless standard for short-range, low-power wireless connectivity. Now, Bluetooth technology enables multiple ways to connect, from simple point-to-point to broadcasting to mesh connections, This expansion of Bluetooth innovation is accelerating new markets like smart buildings.
In 2000, when Bluetooth technology was first commercialized, around 800,000 Bluetooth enabled devices were shipping every year. Today, more than 10 million devices are shipped each day.

How It All Started
Initiated in the early 1990s, Ericsson Mobile in Lund, Sweden laid the groundwork for a short-range radio technology that would support the development of wireless headsets. Shortly thereafter, Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia, and Toshiba formalized the creation of a wire replacement for communicating voice and data between instruments. To ensure the standardization and interoperability of this technology, the founding companies formed the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) in 1998.
“Bluetooth…was possibly one of the most rapid developments of a global creation standard – from idea to commercial deployment.”
By the end of the first year, more than 4,000 companies had signed on as members of the Bluetooth SIG. Today, there are more than 33,000 member companies dedicated to perfecting and advancing a flexible, reliable, and secure wireless connection solution.
“Looking back, Bluetooth® was a remarkable combination of technology and world class technical marketing,” said Glen Collinson, a non-executive director of Blu Wireless Technology and co-founder of Bluetooth pioneer Cambridge Silicon Radio (CSR). “It was possibly one of the most rapid developments of a global creation standard – from idea to commercial deployment – there has ever been.
The Man Behind the Tooth
For how innovative the technology is, the name doesn’t sound techie. Bluetooth® isn’t an acronym and doesn’t stand for anything. Surprisingly, the name dates back more than a millennia to King Harald Bluetooth Gormsson who was well known for two things: Uniting Denmark and Norway in 958 and for his dead tooth, which was a dark blue/grey color and earned him the nickname Bluetooth.
In the mid-nineties, when industry leaders from Intel, Ericsson, and Nokia met to plan the standardization of this technology, Jim Kardash from Intel suggested Bluetooth as a temporary code name. Kardash was later quoted as saying, “King Harald Bluetooth…was famous for uniting Scandinavia just as we intended to unite the PC and cellular industries with a short-range wireless link.”
The name caught on fast and spread throughout the industry, becoming synonymous with short-range wireless technology.
Today, there are more than 33,000 member companies dedicated to perfecting and advancing a flexible, reliable, and secure wireless connection solution.
The Bluetooth Community
“When people think of Bluetooth®, most of the time they are thinking of Bluetooth technology,” said Mark Powell, executive director of the Bluetooth SIG. “But Bluetooth is also a community. An incredible community of member companies that are driving innovation, creating markets, and delivering life-changing value to people around the world.”
Bluetooth member companies collaborate to continually advance the technology. More than 2,300 people involved in over 15 different working groups continue to deliver new capabilities, such as recent speed, range, and broadcast data improvements added with Bluetooth 5, as well as the introduction of mesh networking, which allows tens, hundreds, or even thousands of devices to communicate with one another.
For 20 years, the Bluetooth community has created revolutionary standards and innovative products that have established global markets, shaped culture, and improved lives. After pioneering the wireless audio and connected device markets and ushering in the dawn of the global beacon revolution, the Bluetooth community is developing innovations that enabling intelligent automation across multiple emerging markets, including smart buildings, smart industry, and beyond.



















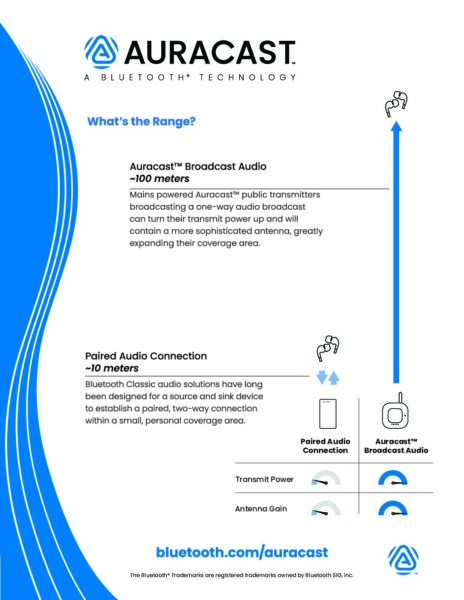
![2312 CES Handout Images FINAL existing pdf 464x600[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/2312_CES_Handout-Images_FINAL-existing-pdf-464x6001-1.jpg)