learn about bluetooth
Bluetooth® Direction Finding
High-accuracy indoor location services
Bluetooth® Direction Finding enables devices to determine the direction of a Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) signal, thereby enabling the development of Bluetooth proximity solutions that can understand device direction as well as Bluetooth positioning systems that can achieve centimeter-level location accuracy.
What is radio direction finding?
Bringing established, time-tested methods for determining signal direction to a proven, trusted radio
Radio direction finding has been in practice since the early twentieth century and is used in systems to support everything from aviation and nautical navigation to wildlife tracking.
Bluetooth Direction Finding brings this well-established practice to one of the most trusted and widely deployed radio technologies in the world.
Bluetooth Direction Finding includes two different methods for determining signal direction, Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD).

Bluetooth® Angle of Arrival (AoA)
Enabling buildings to determine the location of people and things within
In the Angle of Arrival (AoA) method, a transmitting device, such as an asset tag in a Real Time Locating System (RTLS) solution, uses a single antenna to transmit a special signal.
The receiving device, such as a fixed locator, has multiple antenna arranged in an array. As the transmitted signal crosses the array, the receiving device collects data that enables it to calculate signal direction.
Bluetooth® AoA use cases

Asset tracking
Factories tracking material workflow and the location of expensive mobile equipment

Worker safety
Manufacturing facilities ensuring workers do not wander into unsafe areas

Player performance
Sports teams tracking the real-time location and performance of athletes
Bluetooth® Angle of Departure (AoD)
Enabling people and things to determine their location within a building
The Angle of Departure (AoD) method is often described as ‘Indoor GPS’ as it operates in a similar way to outdoor global positioning systems.
In the AoD method, the transmitting device, such as a fixed locator in an Indoor Positioning System (IPS) solution, uses multiple antenna arranged in an array to transmit a special signal.
The receiving device, such as a smartphone, has a single antenna. As the signals from the transmitting device cross its antenna, the receiving device collects data that enables it to calculate signal direction.
Bluetooth® AoD use cases

Indoor Navigation
From airports to museums to convention centers, Bluetooth AoD-based indoor positioning systems can enhance the visitor experience.
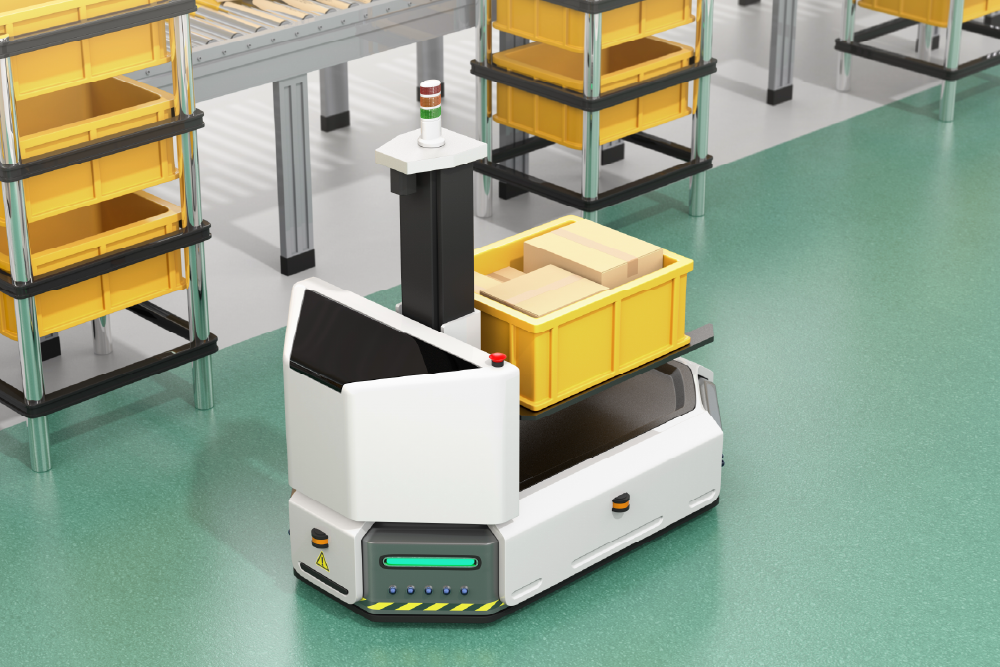

Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs need to know where they are to get where they need to go. Bluetooth AoD-based indoor positioning systems let them know, precisely.