The Evolution of the Positioning Landscape
Much like Bluetooth® technology itself, the location-based services and positioning landscape has evolved significantly over the last couple of decades.
In the early 2000s, automotive navigation and emergency services represented the first generation of the positioning market, where GPS was the dominant enabling technology. Typical requirements exceeded hundreds of meters for accuracy, over one- second latency, and almost no constraints in-terms of power consumption.
A second generation of location-based services emerged in 2010 as smartphones embedded with Bluetooth technology, Wi-Fi, GNSS, and cellular technologies became widely available. This enabled mapping applications for navigation and wayfinding, proximity marketing and advertising, social applications, and, most recently, on-demand delivery services such Uber or Deliveroo. These applications typically require an accuracy of tens of meters and a latency of a few seconds or more.
![]()
The emergence of the internet of things (IoT), in the middle of the last decade, has fueled a third generation of location-based services, targeting specific use cases in the enterprise such as asset tracking, fleet management, and proximity services. Today, the move towards Industry 4.0 together with the emergence of new technologies commonly called real-time locating systems, or RTLS, are now enabling the next wave of location-based services. These promise to locate and track objects and people with a high level of accuracy across both indoor and outdoor environments. Typical solutions enabling these services include GNSS and RTK for outdoor applications; several short-range wireless connectivity solutions, including Bluetooth® technology, Wi-Fi, UWB, and Active RFID for mostly indoor applications; and, in the future, 5G positioning, which seeks to enable more accurate, precise, reliable, and seamless positioning across both indoors and outdoors.
Alongside this, there are growing location-based opportunities in areas such as personal tracking devices, through the likes of Tile, Samsung, and Apple, in addition to other growing use cases, such as secure vehicle entry, access control, smart home interaction, and augmented reality experiences, where location accuracy, reliability, and security is becoming increasingly vital.
These innovations have propelled the positioning ecosystem to grow to billions of device shipments, and it is clear, given the variety of use cases and performance requirements, that no single technology can meet the needs of all these evolving indoor and outdoor positioning applications. Enterprises will require a combination of technologies, including Bluetooth, to solve many of their pain points.
![]()
ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
The Myths & Facts about Bluetooth® Technology as a Positioning Radio
Watch this detailed discussion into the challenges and opportunities in front of indoor location services systems and how to tap into their potential in manufacturing, logistics, retail, offices, and more.
How Can Bluetooth® Technology Help Solve Key Enterprise Pain Points?
Through the precise tracking of both assets and personnel via RTLS, enterprises can potentially save tens to hundreds of billions of dollars globally through enhanced operational efficiencies, increased worker safety, and loss prevention, among other valuable use cases.
For example, in healthcare environments, thousands of lives can potentially be saved if RTLS is used to enforce hygiene compliance to help combat healthcare associated infections (HAI). In the US alone, there are over 80,000 fatalities related to HAIs each year. Meanwhile, tens of billions of dollars related to improved productivity of medical carers and savings from potential loss of equipment can also be made.
Through the precise tracking of both assets and personnel via RTLS, enterprises can potentially save tens to hundreds of billions of dollars globally.
In manufacturing facilities, billions of dollars are lost through unplanned downtime thanks to being unable to locate assets, tools, and equipment. In warehouses, RTLS can help automate the tracking of assets, such as pallets, which is becoming more essential with the ever-increasing size, complexity, and amount of assets stored.
Worker safety applications enabled by RTLS is another growing opportunity. Approximately 35,000 forklift accidents occur every year in the US, resulting in billions of dollars of losses related to compensation, damaged equipment, and downtime. Knowing the precise location of workers and vehicles can help prevent costly accidents.
Essentially, the opportunities for RTLS in the enterprise are almost limitless, and Bluetooth technology is already addressing many of these use cases today. Further improvements to its accuracy through techniques such as Bluetooth Direction Finding, which is already available and in market, will enable it to target some of the more stringent use cases where meter or sub-meter level accuracy is required.
Despite these obvious benefits, the RTLS market remains somewhat of a greenfield opportunity, as only a very small percentage of the potential addressable market in the enterprise has been serviced by RTLS equipment so far.
Several misconceptions around technology performance and viability in certain environments has prevented enterprise decision makers from adopting RTLS technology, and Bluetooth technology is no exception here.
The Myths About Bluetooth® Technology as a Positioning Radio
When discussing the RTLS market with decision makers and technology vendors alike, several myths and misconceptions persist around Bluetooth technology that continue to deter users from adopting it. On 1 March, I attended a webinar hosted by Chuck Sabin of the Bluetooth SIG where myself, Broadcom’s Gabe Desjardins, and Quuppa’s Fabio Belloni discussed some of these and other myths and facts about Bluetooth technology as a positioning technology.
Myth – Bluetooth technology is inaccurate or inferior to alternative positioning technologies
Firstly, and perhaps the most common myth, is that Bluetooth is inaccurate or inferior to alternative technologies, particularly when it comes to accuracy. While historically, RSSI-based solutions have been capable of providing several meters accuracy, Bluetooth technology has recently evolved to support accurate sub-meter, low-latency performance across several different environments via techniques such as Bluetooth Direction Finding (introduced in Bluetooth Core Specification version 5.1). Several Bluetooth RTLS solution providers have deployed these solutions commercially across manufacturing, warehouse, healthcare, sports, and other public venues to date. During the webinar, Fabio demonstrated how Bluetooth Direction Finding solutions are being used within four different ice hockey leagues, tracking the puck, players, and referees with centimeter-level accuracy in real time to provide advanced analytics.
Bluetooth® technology has recently evolved to support accurate sub-meter, low-latency performance across several different environments.
Related to this, Fabio also discussed how the communication range and coverage area for Bluetooth® positioning systems are perceived to be short range only with a perception that if a ceiling is more than ten meters high, Bluetooth solutions do not work well. However, Fabio demonstrated how Bluetooth tags can be tracked by receivers hundreds of meters away. One use case included tracking horses’ riders on a long-distance circuit while another demonstrated tracking football players where the receivers were placed on stadium floodlights.
Of course, there is a strong and evolving competitive landscape in this space, with technologies such as UWB, Wi-Fi, and, in the future, 5G positioning, bringing highly accurate location. However, much like Bluetooth technology, each has its own unique characteristics, deployment requirements, strengths, and weaknesses.
Myth – Bluetooth technology cannot operate well in industrial environments
Closely related to this is the perception that Bluetooth is not capable of performing well in industrial/warehouse environments and is therefore not a reliable technology for RTLS applications. However, Bluetooth® technology is already being deployed in many challenging commercial and industrial environments, enabling use cases where high performance and reliability is required, ranging from forklift and vehicle tracking to worker safety applications, material and asset tracking, and even low-latency sports tracking applications. During the webinar, Fabio also discussed how Bluetooth technology is capable of operating in harsh environments, highlighting several industrial environments where Quuppa technology has already been deployed thanks to the ability of Bluetooth receivers to measure reflections in the spatial domain to resolve multipath issues.
![]()
ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
The Myths & Facts about Bluetooth® Technology as a Positioning Radio
Watch this detailed discussion into the challenges and opportunities in front of indoor location services systems and how to tap into their potential in manufacturing, logistics, retail, offices, and more.
Myth – UWB will replace Bluetooth technology in location applications
With the emergence of Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) technology in smartphones and RTLS applications, a common perception is that UWB will begin to supplant Bluetooth® technology for all positioning use cases. At ABI Research, we certainly believe that UWB will have a fundamental role to play in several location use cases – this will include very high-accuracy, centimeter-level tracking applications within industrial environments, personal tracking devices, secure access applications, and emerging smart home and augmented reality applications. However, not only will Bluetooth technology compete with UWB across many of these use cases, thanks to its improved accuracy and upcoming high-accuracy distance measurement capabilities, but it will also coexist with UWB and, in many cases, it will work alongside UWB to maximize the performance of both technologies to create more scalable positioning deployments.
Many UWB tags on the market today also integrate Bluetooth® LE to support firmware updates and enable smartphone/wearable interaction.
Within the RTLS space, there are a growing number of solution providers who offer a combination of UWB and Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) RTLS infrastructure and tags to be able to provide support for use cases requiring the highest levels of accuracy alongside more scalable asset tracking applications. In 2021, Ubisense, a leader in UWB RTLS solutions, launched its UB-Tag™ with simultaneous UWB and Bluetooth LE tracking capabilities. This aims to provide a more cost-effective combined solution that can target the most stringent applications via UWB and be able to track greater volume of assets via Bluetooth LE. In addition, many UWB tags on the market today also integrate Bluetooth LE to support firmware updates and enable smartphone/wearable interaction.
The two technologies are also working together within emerging secure vehicle entry, access control, and personal tracking use cases. For example, in recent UWB vehicle access deployments, Bluetooth® technology is used by the phone or key fob for initial proximity discovery, thanks to its low power consumption, and then hands over to UWB for secure ranging for the last additional method of authentication and precision at shorter distances. For personal tracking applications, tags are paired via Bluetooth technology and then once Bluetooth detects the tag is within range, it hands over to UWB for more precise detection. Bluetooth technology can also take advantage of its huge installed base of smartphone devices to create personal tracking networks that track lost assets.
In the future, as Bluetooth technology adds increased accuracy and ranging elements, there is also the argument that some vendors may adopt Bluetooth only solutions. As Gabriel highlighted in the webinar, the arrival of channel sounding to provide high-accuracy distance measurement using Bluetooth technology is expected to ship in products in 2023. This will bring significant enhancements for positioning applications, improving the accuracy over existing systems, as well as the security, and is expected to be widely supported by the chipset ecosystem without the need for a new chip or advanced antenna designs. This means that Bluetooth technology’s ranging capabilities will be included as standard and will require a lower investment than UWB with its own dedicated chip.
Bluetooth® technology’s ranging capabilities will be included as standard and will require a lower investment than UWB with its own dedicated chip.
Furthermore, this technology will build on the many Bluetooth® automotive, access control, and personal tracking solutions that exist on the market today. As Gabriel further discussed, Bluetooth technology is already being used in keyless entry and vehicle start applications. Ford launched its Bluetooth Phone as a Key in the 2020 model year and has incorporated it into many of their vehicles. RSSI-based solutions are currently leveraged, but CS/high-accuracy distance measurement will improve accuracy, latency, and the security of Bluetooth solutions as these come to market. Alongside this, it will also take many years before the installed base of UWB devices becomes anywhere near as ubiquitous as Bluetooth technology.
Myth – A single technology will be able to solve all RTLS use cases
This growing combination of technologies helps to dispel another myth – in that there is one single technology that can address all RTLS and positioning use cases. It is important to remember that each positioning use case is unique. Decisions will need to be made on several different metrics. This will include, of course, accuracy but also infrastructure and tag cost, deployment complexity, the number of tracked assets, how frequent assets are being tracked, the deployment environment, battery life, maintenance costs, indoor/outdoor coverage, and whether it needs to interact with smartphones, among others. ABI Research believes that each of these different technologies will have an important role to play depending on each of these specific requirements, and they will often work together.
Myth – Accuracy is the driving factor behind RTLS implementation technology decisions
Perhaps most critically, it is important to emphasize that there is more to selecting a positioning technology than just the accuracy it can provide. Positioning solutions will be evaluated on many of the aforementioned metrics, however, there is a strong obsession within the positioning industry of being able to provide cm or tens of centimeter-level accuracy, which is somewhat distorting the reality of most RTLS use cases. Yes, there will be some use cases that require ultra-high precision centimeter-level accuracy, including AGVs and collaborative robotics applications. However, most use cases will suffice with one to five meter-level accuracy – and many deployments will exist where just knowing what room an item is in, or if it has entered or exited a certain geofenced location, is more than sufficient. Therefore, the industry must begin to shift its attention and efforts away from just talking about centimeter-level accuracy and towards what technologies (and combinations of technologies) can provide reliable, scalable, easily deployable, and cost-effective positioning ecosystems that can transform and digitize the operations of many enterprises.
What Do Industry Verticals Say about RTLS?
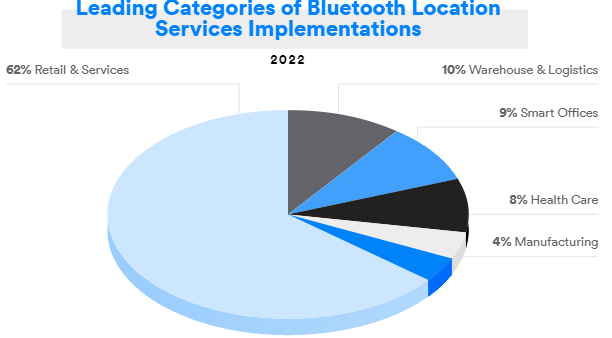
To support this further, ABI Research recently conducted an industry survey involving over 200 decision makers, asking them about their plans for RTLS. Interestingly, 87 percent of respondents said they had not yet deployed RTLS, reaffirming that RTLS remains somewhat of a greenfield opportunity.
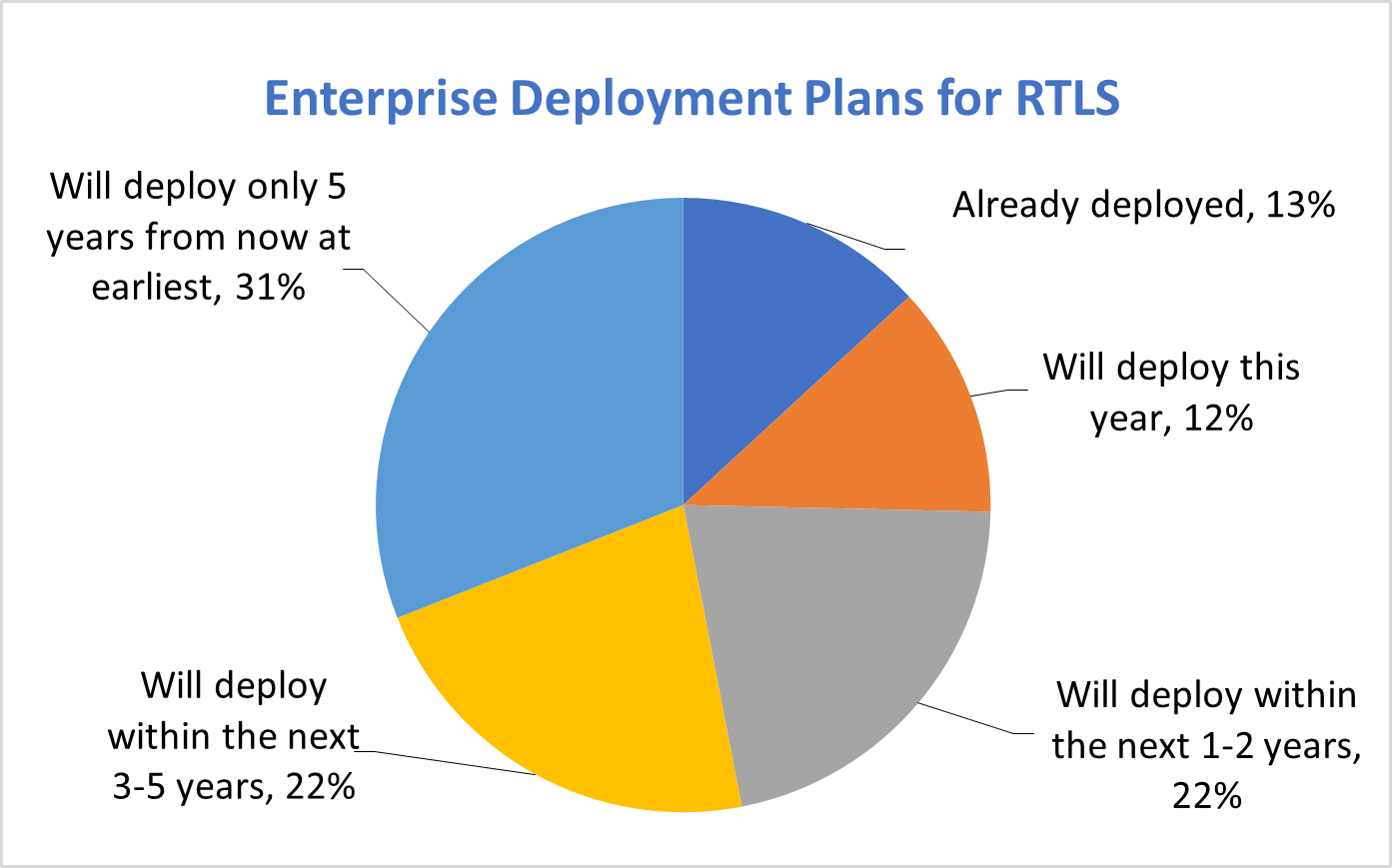
When asked about the barriers to adoption of existing technologies, respondents quoted technology fragmentation, operation and maintenance cost, technology maturity and reliability, and complex implementations as the primary barriers to adoption.
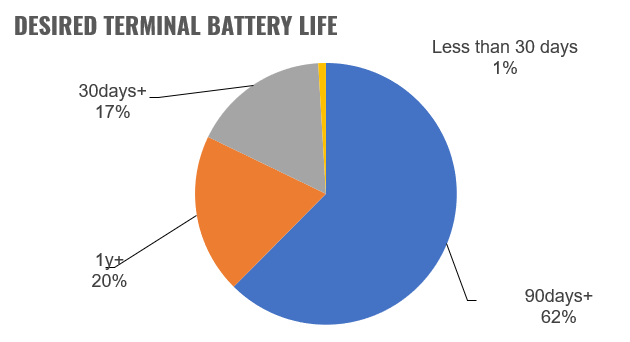
When respondents were asked about desired terminal battery life, 62 percent said that 90 days+ was enough to support their operation, However, a further 20 percent required a year or more, meaning power consumption will remain a key purchasing decision. This places Bluetooth technology in good stead versus competing technologies.
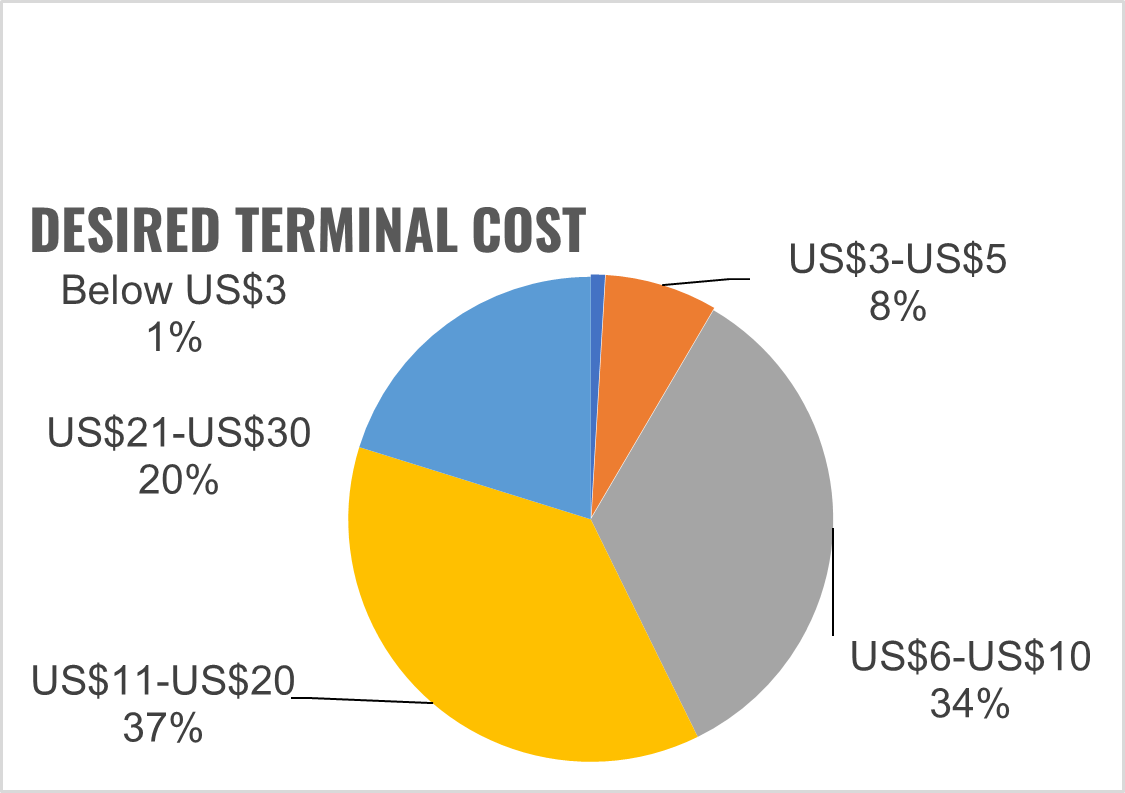
57 percent of respondents said they are happy with a cost of tags to be between $11 and $30. Bearing in mind that some Bluetooth low-energy solution providers provide RTLS tags at below $10 today. This is very encouraging.
However, perhaps most critically, when asked about accuracy, over 2/3 (69 percent) of respondents said that one-to-five-meter accuracy would be sufficient for the majority of the use-cases they want to support. In contrast, only 21 percent of respondents required sub-meter level accuracy, with just four percent of these requiring sub-20cm. Again, the continued emphasis on ultra-high precision accuracy does not reflect the reality of most of the desired positioning requirements on the market today, and Bluetooth technology’s ability to provide flexible, cost-effective solutions from sub-meter to proximity-based levels of accuracy will be vital in helping to scale the market across different use cases.

Bluetooth® Technology is Well Placed for Success in the Positioning Landscape
While indoor navigation and proximity services have led the traditional Bluetooth location market, this will increasingly shift to asset, personnel, and equipment tracking applications. This will result in high-volume tag deployments emerging across healthcare, warehouse and logistics, and manufacturing applications, supporting both RSSI and direction finding performance levels.
At the high level, we expect a 2.5x increase in total Bluetooth RTLS deployments over the next five years, with the fastest growing segments within healthcare, warehouse and logistics, manufacturing, and smart building applications. While ABI Research expects Bluetooth and UWB to be the fastest-growing technologies in the positioning landscape, Bluetooth® technology will continue to dominate tag deployment volumes thanks to its ability to target these growing high-volume use cases, as well as many others in sports, hospitality, offices, public venues, education, personal tracking, and secure access. However, we have still barely scratched the surface of RTLS market’s true potential, which is expected to reach hundreds of billions of tag shipments over the next decade.
Bluetooth technology’s unique capabilities make it well placed to help enable and take advantage of a variety of positioning use cases, whether RTLS, indoor positioning, or personal tracking solutions. The ability to provide RSSI and direction finding, and, in the future, distance measurement, means it can flexibly support a wide variety of use cases with different requirements. This will range from proximity or room level to sub-meter precision, which will account for the majority of positioning use cases, as highlighted by our recent survey. Bluetooth technology also has several advantages in terms of low power consumption, low cost of tags, a ubiquitous mobile presence, a strong chipset and vendor ecosystem, as well as being embedded in Wi-Fi infrastructure to ease the deployment of location services. In addition to competing, Bluetooth will also coexist and cooperate with other technologies, such as GNSS, cellular positioning, LPWAN, UWB, and Wi-Fi, for a variety of reasons, including hybrid positioning, device pairing and handover, firmware updates, and smartphone interaction.
And just to reiterate – there is no one size fits all positioning technology. Bluetooth® technology is well placed to take advantage of many use cases, but so too will UWB, Wi-Fi, 5G, and other positioning technologies, depending on the specific requirements of their positioning use case. Decisions will be made on hardware cost, ease of deployment, maintenance costs, and interaction with smartphones and other devices. What the industry needs to do is to move away from the obsession with ultra-high precision use cases and to come together and develop interoperable ecosystems of positioning technologies that can finally enable scalable deployments of location-based services. Only then will the full potential of the RTLS landscape be realized.
![]()
ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
The Myths & Facts about Bluetooth® Technology as a Positioning Radio
Watch this detailed discussion into the challenges and opportunities in front of indoor location services systems and how to tap into their potential in manufacturing, logistics, retail, offices, and more.
進化を続ける測位技術
Bluetooth® 技術をはじめ、位置情報サービスと測位技術は、この20年で大幅な進化を見せています。
2000年代初め、測位技術市場の第一世代を代表するサービスはカーナビゲーションと緊急通報で、GPSが主たる実現技術でした。代表的な必要条件は、精度数百メートル以上、遅延時間1秒以上、消費電力にいたってはほぼ制約がない状態でした。
2010年になると位置情報サービスの第二世代が登場し、Bluetooth® 技術やWi-Fi、GNSS、セルラーテクノロジーを搭載したスマートフォンが広く利用されるようになりました。その結果、ナビゲーション・経路検索向けのマッピングアプリや近接マーケティング・広告、SNSアプリ、最近ではUberなどのオンデマンドデリバリーサービスが実現しています。ただし、このような利用方法の場合は一般的に、数十メートルの精度誤差と数秒程度の遅延時間が生じます。
2010年代半ばに「モノのインターネット(IoT)」が登場すると、位置情報サービス第三世代の開発が一気に加速し、資産の追跡や物流のフリートマネジメント、近接サービスなど企業向けの特定用途が対象になりました。現在では、「インダストリー4.0」への動きと、リアルタイム位置情報システム(以下、RTLS)と呼ばれる新たな技術の出現が相まって、次世代の位置情報サービスの開発競争が始まり、屋内であれ屋外であれ、モノや人の位置情報と追跡のサービスが高い精度で提供されています。こうしたサービスを可能にする代表的なソリューションは、屋外用としてGNSSやRTK、屋内用ではBluetooth 技術、Wi-Fi、UWB、アクティブRFIDといった短距離ワイヤレスコネクティビティのソリューションが使用されています。今後将来的には、5Gの測位技術との併用により、屋内・屋外にかかわらず、正確度、精密度、信頼性が向上した、よりシームレスな測位情報の提供が可能になります。
その動きに並行して、個人用の追跡デバイスのような分野では、TileやSamsung、Appleなどを利用した位置情報のビジネスチャンスも拡大しており、ほかにも安全な車両入出庫、アクセスコントロール、スマートホーム・インタラクション、AR(拡張現実)といった事例が増加しています。いずれの事例でも、位置情報の高い精度、信頼性、安全性はその重要度が増しています。
こうしたイノベーションで測位技術は、関連するテクノロジーも含め成長が加速し、数十億というデバイスが出荷されています。また、多種多様な使用事例や性能要件を考えると、単一技術では、進化を続ける屋内・屋外のあらゆる測位サービスのニーズを満たせないのは明らかです。今後、テクノロジー企業には、Bluetoothをはじめ複数の技術を効果的に組み合わせてさまざまな課題を解決することが求められていくでしょう。
Bluetooth技術は、企業が抱える大きな課題の解決にどのように役立つのですか?
資産も人も、RTLSを利用して高精度な追跡を実施すれば、世界規模で数百億ドルから数千億ドルのコスト削減も決して不可能ではありません。利用方法は多岐にわたり、経営効率や従業員の安全性の向上、損失の防止をはじめとして役立つものが数多くあります。
たとえば医療現場では、米国だけでも毎年8万人を超える市民が医療関連感染(HAI)で命を落としていますが、RTLSが利用されると、衛生遵守が徹底されて、HAIとの闘いに役に立ち、何千という生命が救われる可能性があります。その一方で、医療従事者の生産性向上と、医療機器の潜在的損失のさらなる削減で、何百億ドルも節減できるようになります。
資産も人も、RTLSを利用して高精度な追跡を実施すれば、世界規模で数百億ドルから数千億ドルのコスト削減も決して不可能ではありません。
製造現場では、資産やツール、製造機器の位置情報を把握できない結果、計画外のダウンタイムで何十億ドルという損失が生じています。倉庫でRTLSを活用すると、パレットなどの資産の自動追跡が可能になります。保管する資産でサイズ・種類・量の複雑化が進むなか、RTLSの重要性が高まりを見せています。
RTLSを利用した、従業員の安全を守るアプリも人気が高まっています。米国ではフォークリフトで毎年約3万5000件の事故が発生しており、補償や機材の損傷、ダウンタイムで、数十億ドルもの損失が生じていますが、従業員や車両の位置が正確にわかれば、コストのかかる事故の防止が可能になります。
そもそも企業向けのRTLSは、ほぼ制限なく利用できます。実際、Bluetooth技術はすでに、そうした使用事例で数多く採用されています。Bluetooth Direction Finding(Bluetooth方向検知機能)のような技術でRTLSの精度がさらに向上すれば、メートル単位もしくはサブメートル単位の精度が必要とされる厳しい使用事例も対象とすることも可能になります。
このようにRTLSには明らかなメリットが複数あるにもかかわらず、RTLS市場のビジネスチャンスは依然としてある意味手つかずのままであり、これまでのところRTLSのサービスが提供されているのは、企業向けの潜在的な市場のなかでもほんのわずか割合にすぎません。
特定の環境におけるテクノロジーの能力や実行可能性に関しては、いくつか誤解がありますが、そうした誤解により、企業の意思決定者はRTLSテクノロジーの採用を避けてきました。そして、Bluetooth技術もその例外ではありません。
測位用無線としてのBluetooth®技術に関する誤った定説
企業の意思決定者やテクノロジーベンダーと話していると、Bluetooth技術に関していくつかおかしな定説や誤解がしつこく残っていることがよくわかります。ユーザーがBluetooth技術の採用を躊躇し続ける原因はそこにあります。3月1日、私はABI Researchのアンドリュー・ジグナニと共に、Bluetooth SIGのチャック・サビン氏がホスト役を務めるウェビナーに出席し、Broadcomのガブリエル・デジャルダン氏およびQuuppaのファビオ・ベローニ氏と4人で測位技術としてのBluetooth技術について、そうした誤解や通説、さらには事実について論じました。
誤った定説――Bluetooth技術は正確ではない、ほかの測位技術と比べると劣っている
最初に取り上げるのは、おそらく最もよく知られている誤った定説「Bluetoothは、こと精度に関しては正確ではない。ほかの測位技術よりも劣っている」です。これまでのところ、RSSI系ソリューションは誤差が数メートルという高い精度を誇っていましたが、ここにきてBluetooth技術が進化を遂げました。Bluetooth Direction Finding(Bluetoothコア仕様バージョン5.1で導入)のようなテクノロジーを駆使して、複数の環境下でも、精度がサブメートル単位、遅延時間がほとんどない低レイテンシーを実現しています。Bluetooth RTLSソリューションのプロバイダー数社はこれまでのところ、こうしたソリューションを製造や卸売、医療、スポーツのほか、公共施設にも販売しています。今回のウェビナーでは、ベローニ氏がBluetooth Direction Findingソリューションがいかにしてアイスホッケーの4リーグで使用されているのかを見せてくれました。そのデモンストレーションで、このソリューションが、パックや選手、審判をセンチメートル単位の精度でリアルタイムに追跡し、高度なアナリティクスを提供していることがよくわかります。
ベローニ氏はこれに関連して、Bluetooth®測位システム用通信範囲と通信エリアは近距離だと考えられるのは、天井の高さが10メートル以上あると、Bluetoothのソリューションはうまく機能しないと認識されているときだけだという件についても言及しています。しかし実際のところ、Bluetoothのタグは数百メートル 離れた場所にある受信機でも追跡可能であることを説明し、具体的に、距離の長いコースでも騎手の追跡が可能であること示す事例や、受信機をスタジアムの投光器に置いてサッカー選手を追跡する事例を紹介しました。
進化を遂げるBluetooth技術。複数の環境下でも、精度がサブメートル単位、かつ遅延時間がほとんどない低レイテンシーを実現。
もちろんこの分野には、進化を続ける強力な競合が存在し、UWBやWi-Fi、それに将来的には5Gの測位システムといった技術が極めて精度の高い位置情報をもたらします。しかしながら、どの技術にもその技術特有の特徴や導入要件、強み、弱みがあります。Bluetooth技術にも当然あります。
誤った定説――Bluetooth技術は生産現場では効率よく使えない
この定説と強く結びついているのが、Bluetoothは工場や倉庫で性能を発揮できず、その結果、RTLS用技術としては信頼できないという認識です。しかしながら、Bluetooth® 技術はすでに商業施設や工場といった要件の厳しい現場に数多く投入されています。その事例は高い性能と信頼性が求められるものであり、フォークリフトや車両の追跡から、従業員の安全を守るアプリ、資材や資産の追跡、低遅延スポーツ用追跡アプリまで多岐にわたります。ベローニ氏は今回のウェビナーで、Bluetooth技術が厳しい環境でも対応できることを説明しました。たとえば、空間領域における反射測定が可能なBluetooth受信機のおかげで、Quuppa技術が導入され、マルチパスの課題解決に取り組むことができた複数の工場を紹介しています。
誤った定説――UWBは位置情報アプリでBluetooth技術に取って代わるだろう
スマートフォンやRTLSで使用されている超広帯域無線通信(UWB)技術の出現に伴い、「今後、測位のあらゆる使用事例でUWBがBluetooth®技術に取って代わり始めるだろう」というのが一般的な認識です。弊社ABIリサーチも、確かに一部の位置情報の事例でUWBが基本的な役割を果たすだろうと考えています。たとえば、業務用のセンチメートル単位に超高精度な追跡アプリや個人用の追跡デバイス、安全なアクセスアプリ、新たなスマートホームや拡張現実のアプリもその一部です。しかしながら、Bluetooth技術は精度が向上したうえに、近々、高精度な測距能力もプラスされるため、こうした数多くの事例では単にUWBと競争関係になるだけではなく、UWBと共存することになるでしょう。そして、多くの場合、UWBと共に機能して、双方の性能を最大限に活かし、より拡張性の高い測位サービスを作り出していきます。
RTLSの分野では、UWBとBluetooth Low Energy (LE)のRTLSインフラとタグを組み合わせて提供するソリューションプロバイダーが増えています。こうしたプロバイダーは、より拡張性の高い資産追跡を可能にするだけでなく、最高レベルの精度が必要とされる事例もサポートできます。2021年、UWBのRTLSソリューション大手のUbisenseが、UWBとBluetoothのトラッキング能力を同時に兼ね備えたUB-Tag™ を発売しました。その目的は、より費用対効果の高い複合ソリューションの提供にあります。つまり、UWBでは最も厳格なアプリケーションを対象にして、Bluetooth LEでは追跡可能な資産の量を増やせるということです。さらに、現在市販されている多くのUWBタグも、Bluetooth LEが統合されているので、ファームウェアのアップデートのサポートや、スマートフォンやウェアラブル端末の利用が可能になります。
現在市販されている多くのUWBタグも、Bluetooth LEが統合されているので、ファームウェアのアップデートのサポートや、スマートフォンやウェアラブル端末の利用が可能になります。
この2つのテクノロジーは、安全な車両入出庫やアクセスコントロール、パーソナルトラッキングといった新たな事例でも相互補完しています。たとえば最近のUWB車両アクセスの事例では、最初にスマートフォンやスマートキーでBluetooth®技術を使い、消費電力を抑えて近接検知が行なわれると、そのあとは安全に測距を行うUWBに引き継がれ、より近距離で認証を行い、精度を高める最後の追加ステップに移ります。個人用の追跡アプリの場合、タグはBluetooth技術とペアリングして使用されます。いったんBluetoothが通信範囲内にタグがあることを検知すると、UWBに引き継がれ、UWBがさらに精度の高い検知を実施します。スマートフォンという巨大なインストールベースもBluetooth技術のメリットであり、なくなった資産の追跡を行う個人用の追跡ネットワークを作ることができます。
将来的には、Bluetooth技術が精度と測距を高めれば、Bluetoothのみのソリューションを採用するベンダーが出てくる可能性もあります。デジャルダン氏がウェビナーで強調しているように、2023年には、Bluetooth技術を利用して高精度測距を実現するチャネルサウンディングが製品に搭載されるようになります。その結果、測位アプリは品質が大幅に向上し、既存のシステムは、安全性はもとより精度も高まります。また、新たなチップや上位アンテナは必要ないので、チップセット関連業者で広く支持されるようになるでしょう。それはつまり、Bluetooth技術の測距が標準に組み込まれ、専用チップが必要なUWBよりも投資が少なくて済むことを意味します。
さらにこの技術は、現在市販されている、数多くの自動車やアクセスコントロール、個人用追跡といったBluetooth®のソリューションにも搭載されることにもなるでしょう。デジャルダン氏も論じているように、Bluetooth技術はすでにキーレスエントリーやエンジン始動の用途で使用されています。フォードは2020年式にキーとしてBluetooth Phoneを導入、それ以降、多くの車両に使用しています。現在活用されているのはRSSIを利用したソリューションですが、CS/高精度距離測定が市場に出回るにつれて、Bluetoothソリューションの精度・遅延・安全性は高まるでしょう。その一方で、UWBデバイスを搭載した基盤がBluetooth技術のようにどこででも見られるようになるには、まだ何年も時間がかかるでしょう。
Bluetooth®技術の測距が標準に組み込まれ、専用チップが必要なUWBよりも投資が少なくてすみます。
誤った定説――単独のテクノロジーですべてのRTLS使用事例が解決可能になる
このところテクノロジーの融合を目にする機会が増えているおかげで、一つの誤った定説が消えかかっています。その定説とは、「すべてのRTLSや測位に対応できる単独のテクノロジーがある」です。測位の事例はどれ一つとして同じものはないと心しておくことが肝要です。決断は、複数の数字を見て下さなければなりません。その数字にはもちろん精度も含まれますが、その他にもインフラやタグのコスト、導入の複雑さ、追跡対象となる資産の数、追跡頻度、導入環境、バッテリーの寿命、メンテナンス費用、対象となる場所(屋内/屋外)、スマートフォンとのインタラクションの必要性などさまざまな項目があります。ABI Researchは、今後、こうした様々な技術がそれぞれの仕様要件に応じて重要な役割を担い、相互に補完することも少なくないだろうと考えています。
誤った定説――精度はRTLS導入技術を決める一番重要な要因である。
おそらく何よりも重要なのは、測位技術を決めるときには、その技術の精度だけでなくそれ以外にも多くの要因があることを忘れてはならない点です。測位ソリューションは前述の数字の多くで評価されますが、測位業界には、精度をセンチや数十センチで示さなければならないという強迫観念が生じており、それが、実際にRTLSが導入される現場の真実を少しばかり歪めています。もちろん、無人搬送車や協働ロボットで使用する場合など、センチメートル単位の超精密な精度が求められる事例が決してないわけではありません。しかしながら、ほとんどの場合は1メートルから5メートル程度の精度で十分です。それに、現場の大半は、「モノが今どの部屋にあるのか」、「ジオフェンスの中に入ったのか、外に出たのか」さえわかればそれで十分というのが現実です。そのため、業界は注目すべきポイントや取り組みをセンチメートル・クラスの精度に固執するのをやめて、どのような技術が(さらには、どのような技術の組み合わせが)、信頼性、拡張性、展開の簡易性が高く、費用対効果のよい測位関連の環境を提供してくれるのかにシフトし始めなければなりません。そうした環境が多くの企業の業務を変えて、デジタル化へとつながるのです。
業界の人々はRTLSについてどう考えているのか?
前述の意見をさらに補強するために、ABI Researchでは200人を超える意思決定者を対象とした業界調査を実施し、RTLSの計画について尋ねました。おもしろいことに、回答者の87%がまだRTLSを利用したことがないと回答し、RTLSのビジネスチャンスは依然としてある意味「手つかずのまま」であることが確認できました。
既存技術の採用で障害になることを尋ねたところ、テクノロジーの細分化、運用・メンテナンスのコスト、テクノロジーの成熟度と信頼性、複雑な導入作業が採用の主な障壁として挙げられました。
バッテリーの理想的な寿命について尋ねたところ、62%が90日余りあれば運用に役立つと回答しています。その一方で、20%の回答者は1年以上を必要としており、ここから、引き続き電力消費量が購買の決め手であることがわかります。この点ではBluetooth技術が秀逸です。競合技術よりも効果的です。
タグのコストに関しては、57%が11ドルから30ドルが無難だと回答しています。Bluetooth LEソリューションのプロバイダーには、現在、RTLSのタグを10ドル以下で提供しているところがあることを考えると、これは実に心強い傾向です。
しかしながら何よりも重要なのは、精度の質問に対して、3分の2以上(69%)が利用したい用途の大半は1~5メートルの精度があれば充分であると回答している点です。対照的に、サブメートル単位の精度が必要な回答者は21%にとどまり、20センチメートル以下の精度が必要だとする回答者はわずか4%にすぎませんでした。ここでもまた、超高精度に固執しても、現在の市場で望まれる測位の必要条件の現実を反映しているとはいえないことがわかります。また、精度がサブメートルから近接レベルまで用意され、柔軟性に富み、費用対効果のよいソリューションを提供できるBluetooth技術は、さまざまな利用方法がある市場のスケールアップを支えるのに極めて重要です。
測位サービスで成功を収めたいのなら、Bluetooth®技術が最適
これまでのBluetooth位置情報サービス市場は屋内ナビゲーションサービスや近接サービスが牽引してきましたが、今後は、資産・人・機材の追跡アプリに大きくシフトしていくでしょう。その結果、医療、倉庫や物流、製造の現場ではタグが相当量利用されるようになり、RSSIと方向検知機能の両方をサポートしていきます。
ABI Researchによる調査の上位を見ると、今後5年でBluetooth RTLSの利用が全体で2.5倍増加し、利用が著しく伸びる分野は医療、倉庫・物流、製造、スマートビルディングであると予測されています。測位サービスで最も急成長を遂げる技術はBluetoothとUWBだと考えますが、タグの利用量が多いのはBluetooth®技術になるでしょう。これは、Bluetooth®技術がスポーツや病院、事業所、公的施設、教育、個人用の追跡、安全なアクセスで利用されるだけでなく、Bluetoothには先の急成長を遂げる分野を対象とする能力があるからです。その一方で、RTLS市場は潜在能力についてまだ十分な調査が行われていないものの、今後10年で出荷されるタグは1000億個に届くのではないかと見ています。
Bluetooth技術はその独自の性能で、RTLSであれ屋内測位であれ個人用追跡であれ、さまざまな測位ソリューションの実現や利用のサポートで適切な役割を果たしています。RSSIや方向検知機能のサービスが提供可能で、将来的には測距も計画されているので、さまざまな要件の使用事例にも柔軟に対応できます。直近のABI Researchの調査で指摘しているように、その対応範囲は近接検知や、部屋単位からサブメートル級の精度まで幅広く、測位事例の大半が含まれます。Bluetooth技術はWi-Fiインフラへの埋め込みが可能で、位置情報サービスが容易く提供できるだけでなく、低消費電力をはじめ、タグのコストがあまりかからない、場所を選ばずに使える、チップセットとベンダーの関係が盤石であるなどの利点もあります。また、今後は、GNSSや測位用セルラーテクノロジー、LPWAN、UWB、Wi-Fiをはじめとする他のテクノロジーとは競争するだけでなく、ともに共存、協働していくことになるでしょう。こうした技術は、たとえばハイブリッド測位システム、デバイスのペアリングや移行、ファームウェアの更新、スマートフォンとのインタラクションなどで利用が可能となります。
繰り返しになりますが、あらゆる測位サービスに適合する唯一無二のテクノロジーなど決して存在しません。確かに、Bluetooth技術はさまざまな事例で有効に活用されていますが、同じことがUWBやWi-Fi、5Gなどほかの測位テクノロジーにもあてはまります。すべて測位事例の仕様要件次第なのです。テクノロジーの選択は、ハードウェアのコスト、利用の容易性、メンテナンスのコスト、スマートフォンやほかのデバイスとのインタラクションで決まります。今この業界に必要なのは、超高精度でなければならないという強迫観念から離れることであり、測位技術の環境を皆で協力して創出し、発展させていくことです。そうすれば、最終的には位置情報サービスのスケールアップが可能になります。RTLSの潜在能力がすべて明らかになるのは、それが実現したあとの話です。